- Chapters
-
Chapter 2
Sections - Chapter 2 Home Page
- Chapter PDF
Chapter 2
Quick Links
2.3.1
Assessing Current Practice
An assessment of current agency competency against industry-leading practice enables an agency to assess a desired future performance level. It can also help to identify the steps required to reach that goal.
TAM is an evolving process; ongoing improvement is an important component for a TAM program. In fact, the ISO 55001 Asset Management certification requires ongoing assessment and continual improvement.
A gap assessment process is used to understand how well an agency aligns with an established asset management framework. The gap assessment can be conducted internally or by a third party. Organizations seeking or wanting to maintain ISO certification will also undergo a formal third party audit.
The results of a gap assessment can help agencies identify changes in business processes needed to better link plans and decisions and better align to leading practice.
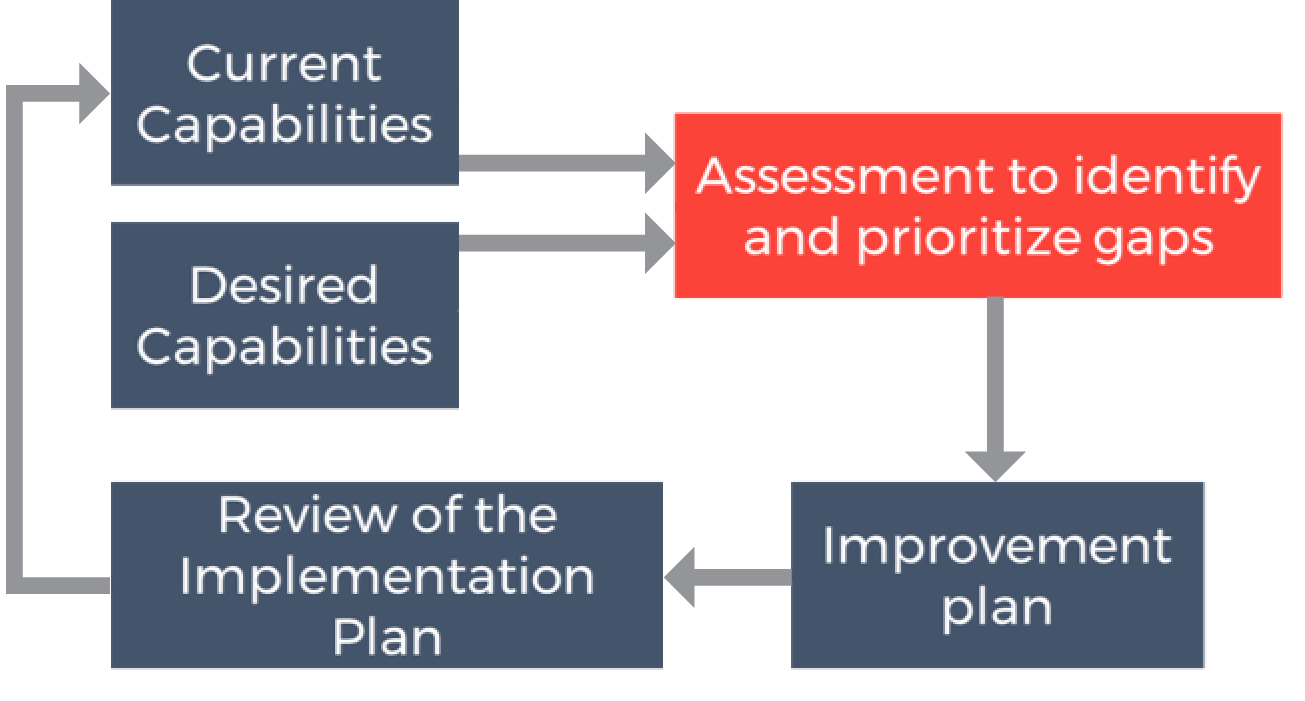
NCHRP Project 08-90 led to the development of a gap analysis tool, available through AASHTO and the TAM Portal. Figure 2.8 illustrates how this assessment tool is intended to be used. There are several other frameworks that can be used, including ISO 55001 and the Institute of Asset Management (IAM). A range of gap assessment framework’s are discussed further in Table 2.1. Each framework, process or tool will enable an agency to assess current performance and, from this, identify a desired capability level.
Figure 2.8 TAM Improvement Cycle
Source: Modified from original in NCHRP Project 08-90
TIP
Factors to consider when prioritizing advancement in TAM approaches will vary from agency to agency. Consider those factors that are of most importance to you and are well-aligned to your strategic goals.
In some cases, agencies also seek benchmarks that reflect how peers are performing to help them decide on the level of maturity and complexity to which they should aspire. ISO 55001 trends away from this. It encourages agencies to check against a framework of practices and process, and select what is best for the agency. Chapter 6 addresses benchmarking and related topics.
Actions to close gaps between desired and actual performance should be addressed within a TAM improvement or implementation plan.
Undertaking a gap assessment can form an important part of a change management process by aligning those within the agency on current performance, opportunities and targets for improvement.
Table 2.1 - Frameworks for Assessing Current Practice
| Framework | NCHRP 08-90 Gap Analysis Tool | ISO 55001 Asset Management Gap Analysis | International Infrastructure Manual (IIMM) | IAM Self-Assessment Methodology |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Background | This tool was developed based on the tool and process created through development of the 2011 AASHTO TAM Guide. Uses a point scale for evaluating current and desired capabilities. See more | This is the most widely adopted standard for asset management globally. It is generic to accommodate many contexts. Describes a management system approach to asset management. See more | Recognizing that the ISO Standards for asset management are very much the “What to do”, the IIMM looks to provide the “How to do it”. Identifies an Asset Maturity Index (Aware, Basis, Core, Intermediate, Advanced) to identify the current and an appropriate level of asset management for each asset. See more | As an aid to the application of ISO 55001, the IAM decided to update their methodology into one that enables organizations in all sectors to measure their capabilities against the requirements of both PAS 55 and ISO 55001. See more |
| Assessment or Focus Areas |
|
|
|
|
| Why use this framework? | This framework is best for an agency that wants to work explicitly within a US-defined context that adopt wider influences. Since this tool can be fully customized by an agency, an agency that wants to tailor the analysis to their particular needs will find this useful. Finally, the tool facilitates the analysis of data, and can generate graphs and charts using the data imported into it. | This framework is ideal for agencies that want to adopt a world-recognized approach to asset management that provides a developed asset management lexicon. This is currently the most internationally-recognized standard in the world. | This framework has been refined over time with many examples that illustrate successful application of concepts by organizations. Public agency focused, and largely written for the asset management practitioner responsible for civil assets. | This standard is well recognized internationally, is infrastructure agnostic, and has applicability to infrastructure owners in both the private and public sector. It has many other resources developed along with the framework including training materials, reference guides and courses to upskill an agency. |
Amtrak
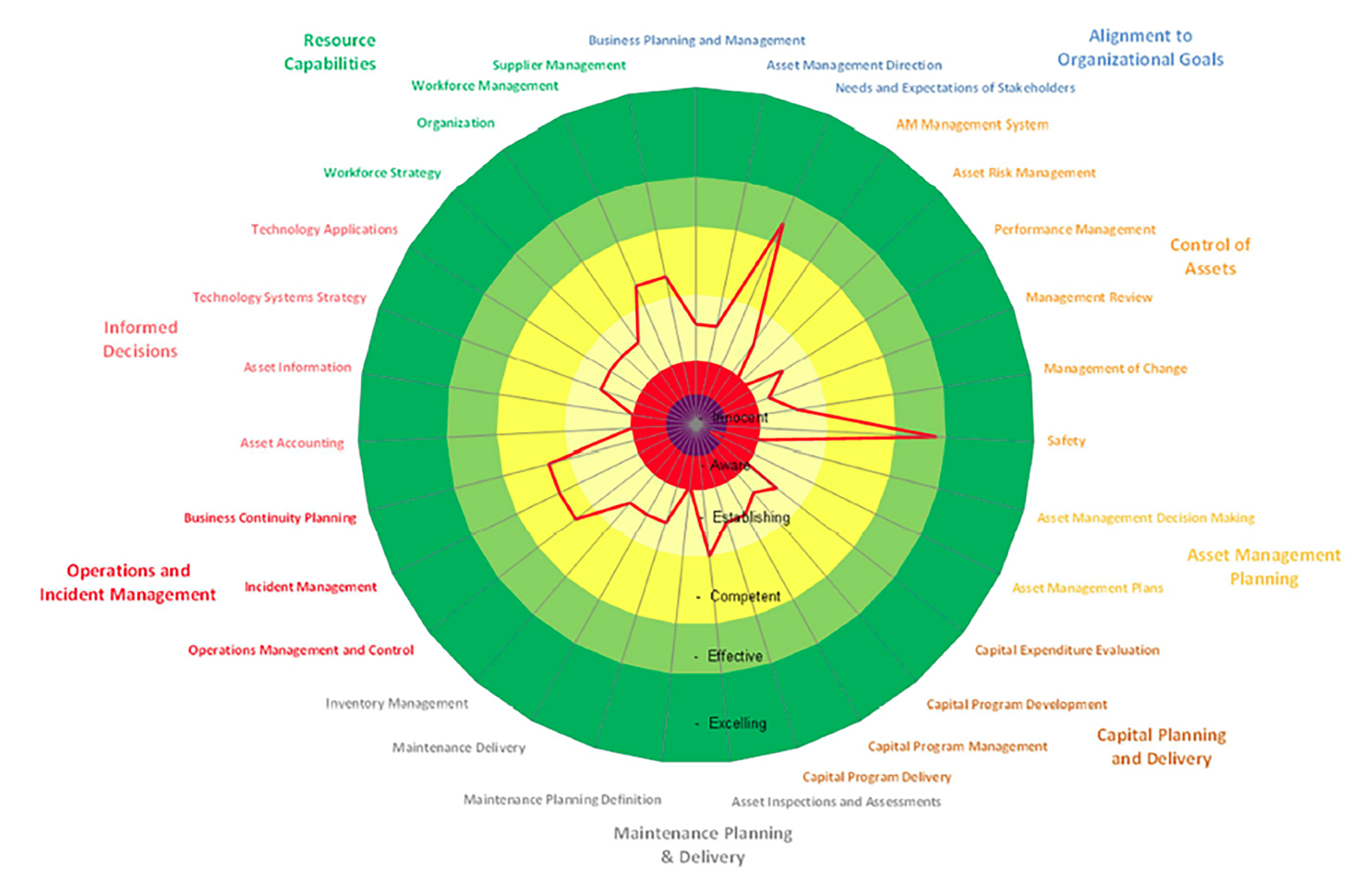
In 2016, Amtrak Engineering undertook an Asset Management Capability Assessment which bases maturity on the degree of formality and optimization of processes. The assessment uses several questions grouped into eight assessment areas, which describe operational processes necessary for asset management success. This maturity methodology is aligned with emerging guidance from the Institute of Asset Management (IAM), ISO 55001 standards, and requirements of the US FAST Act.
The assessment used a six-point scale, scoring Amtrak at the Establishing level, indicative of an agency that is actively developing asset management capabilities and establishing them to be consistent, repeatable, and well-defined.
Based on the 2016 assessment results, key challenges were identified and a series of improvement recommendations were developed and integrated into an Asset Management Improvement Roadmap.
In addition, Amtrak established a target position, driving process implementation priorities, with the intention of continuous monitoring by repeating the capabilities assessment process on an annual basis.
2016 Amtrak Asset Management Capabilities Assessment Results
Source: Amtrak Engineering 2019