- Chapters
-
Chapter 1
Sections - Chapter 1 Home Page
- Chapter PDF
Chapter 1
Quick Links
1.4.1
Gap Analysis Tool Data Structure
This subsection introduces the TAM Gap Analysis Tool designed for agencies to self-assess their Transportation Asset Management (TAM) practices. It outlines the tool's purpose, including comparing practices against industry standards, identifying gaps, recognizing areas for improvement, prioritizing action items, and monitoring TAM maturity over time. The tool operates at three levels—Assessment Areas, Assessment Elements, and Assessment Criteria—covering eight broad topic areas related to TAM practices, each with specific elements and criteria for evaluation during the gap analysis process.
Note: This section was derived from the AASHTO TAM Portal. The TAM Gap Analysis Tool, User Guidance, and additional information are available here: https://www.gapanalysis.tam-portal.com/sign-in/?next=/
Introduction
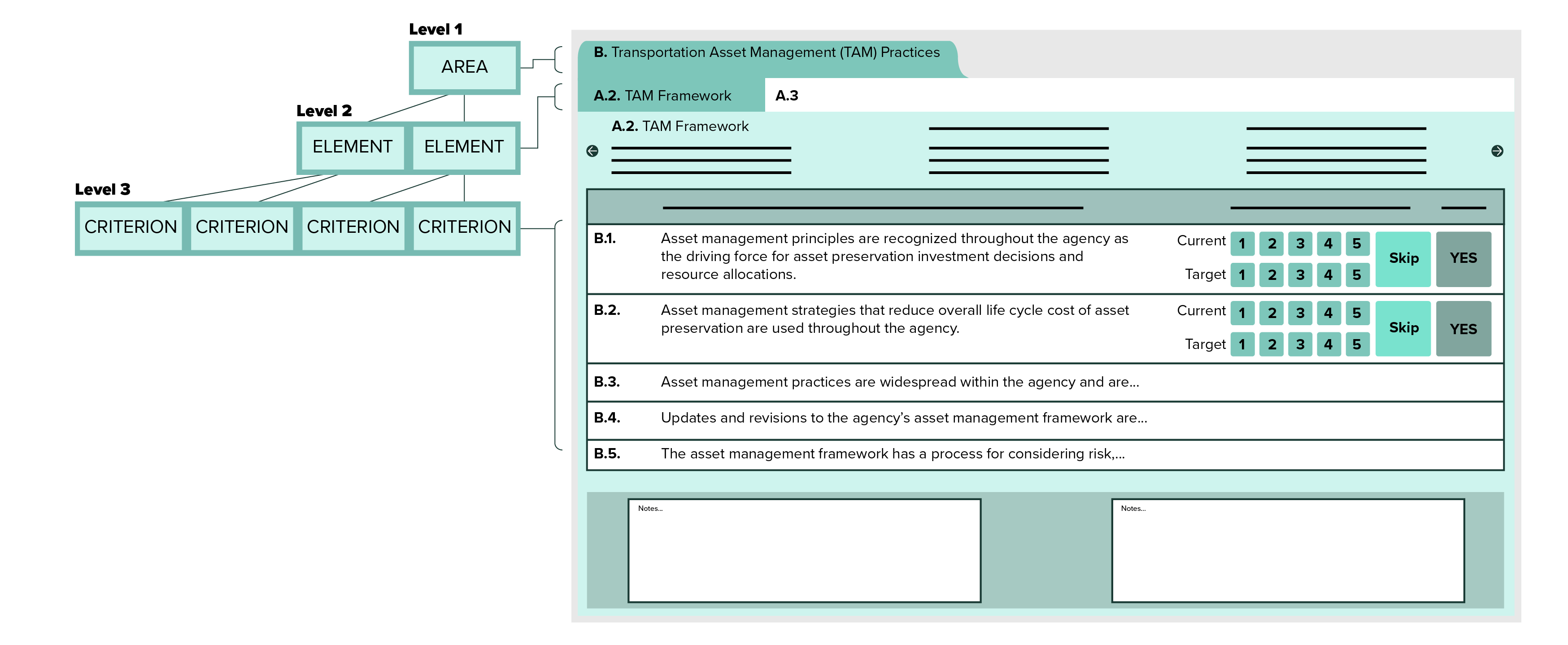
The Gap Analysis Tool supports analysis at three different levels as shown in the figure and described below.
Figure 1.6 TAM Gap Analysis Tool Demonstration
Level 1: Assessment Areas. The highest level is the Assessment Area, which includes eight topic areas:
- Policy goals and objectives.
- Asset management practices.
- Planning, programming, and project delivery.
- Data management.
- Information systems.
- Transparency and outreach.
- Results
- Workforce capacity and development.
Level 2: Assessment Elements.Each Assessment Area has been subdivided into two or more Elements, which can be considered subsets of each of the eight broad topic areas. The tool supports each element with general recommendations for agency practice improvement, and provides the option to share custom language to support agency user benchmarking decisions.
Level 3: Assessment Criteria. Within each Element, there are two or more criteria that are used to evaluate current and desired practice. Each criterion is presented as a standard statement representing good practice. The tool allows the assessment facilitator to adjust the criterion language as needed to promote understanding by the assessment participants.
During the gap analysis, participants evaluate how closely their agency’s practices match what is described in each criterion. This rating is considered representative of the agency’s current practices. Agencies may also define how closely they want to reflect the practices described in each criterion. This rating represents the agency’s desired practices. The difference between the current and desired practices determines whether a gap exists.
The number of Elements and Criteria within each of the eight Assessment Areas are shown in the table below.
Table 1.1 Assessment Areas of TAM GAP Analysis Tool
| Assessment Areas | Elements and Number of Criteria |
|---|---|
1: Policy Goals and Objectives |
|
2: Asset Management Practices |
|
3: Planning, Programming, and Project Delivery |
|
4: Data Management |
|
5: Information Systems |
|
6: Transparency and Outreach |
|
7: Results |
|
8: Workforce Capacity and Development |
|