Decision Making Context
Life cycle management is driven by the need for owners to provide consistent service to those that use the transportation system with the resources available. Infrastructure decision making can take place at several levels within an organization, and in each case, considers different but often interrelated factors. These are illustrated in table 4.1.
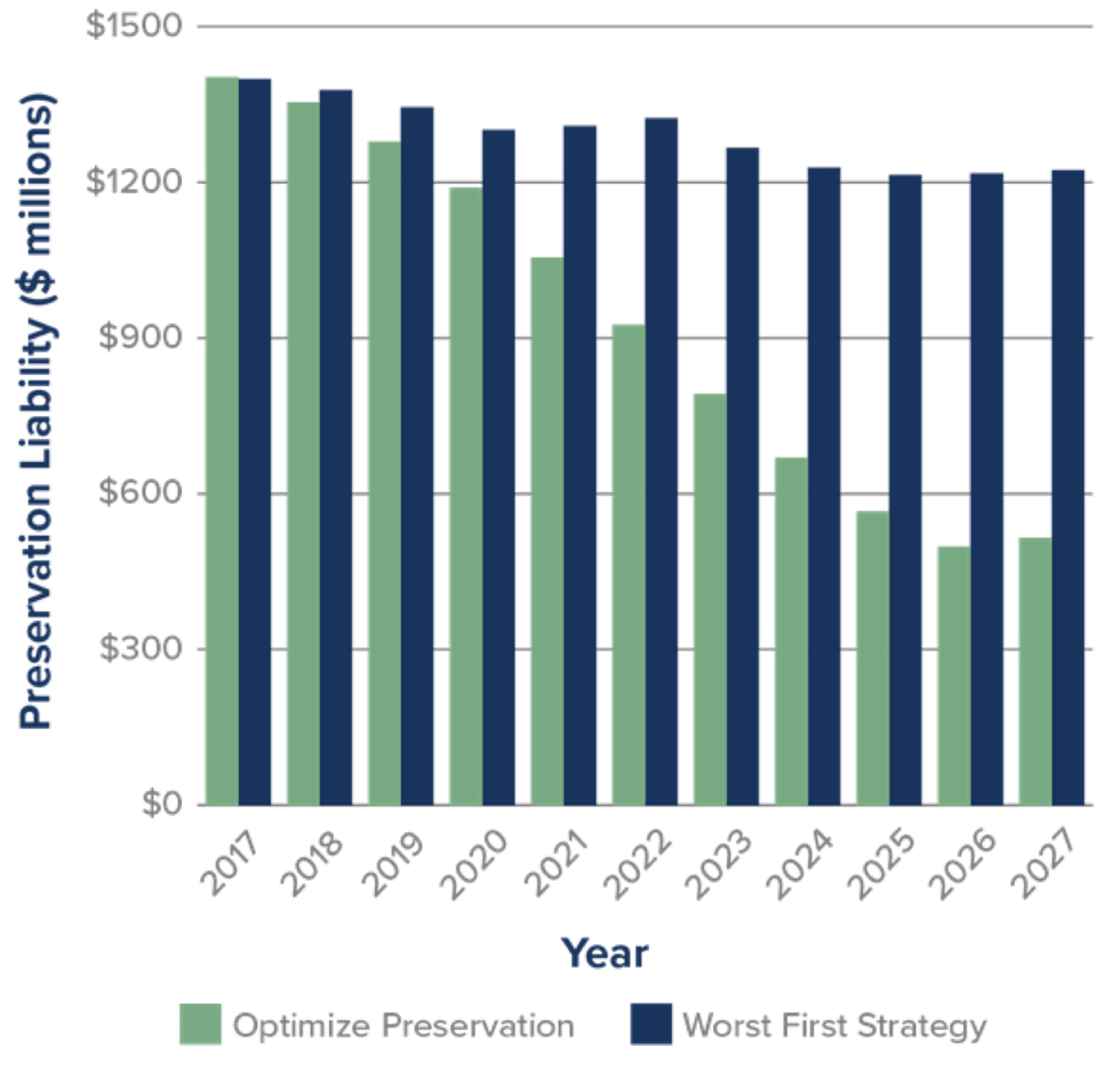
Figure 4.3 Analysis of KYTC Future Costs Under Two Strategies
Source: Kentucky Transportation Cabinet Transportation Asset Management Plan, 2018.
Table 4.1 - TAM Decision-Making Contexts
Key Questions and Connections to Other Chapters
| Strategic | Tactical | Operational | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Key Decisions | Setting goals and objectives. | Capital investment prioritization and scoping and Integration of maintenance and renewal strategies | Delivery of the capital program, routine maintenance, and highway-operations activities. |
| Decision Makers |
| Directors and managers who are asset stewards. | District and field mangers, supervisors, and staff. |
| Key Questions |
|
|
|
| Other Factors | Decisions and outcomes of these strategic questions help focus investment. They add value to overall performance of the transportation system by setting priorities, values, and help prioritization of investment at lower levels. Creating new assets and disposing of existing ones are strongly influenced by decisions and priorities defined at this level. Chapter 2 discusses these considerations in more detail, and the level of service section in this chapter discusses linking these strategic priorities to decision-making at lower levels. Performance and target setting in Chapter 6 also discusses this linkage and how targets can be set to achieve these strategic goals. | This Chapter focuses on these questions and on the analysis that informs their corresponding answers and decisions. Life cycle management and analysis focuses on the existing transportation system and evaluates how:
| Delivering a program work, ranging from maintenance activities to capital improvements, requires a coordinated management of a large workforce. It requires processes that minimize input of resources to get the output required for desired system performance. Work management systems, efficiency and improvement techniques and performance management focus on improving decisions at this level. These concepts are discussed in Chapter 5, 6 and 7. |